1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
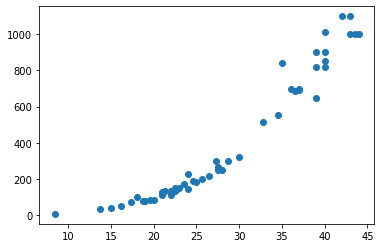
| import numpy as np
perch_length = np.array(
[8.4, 13.7, 15.0, 16.2, 17.4, 18.0, 18.7, 19.0, 19.6, 20.0,
21.0, 21.0, 21.0, 21.3, 22.0, 22.0, 22.0, 22.0, 22.0, 22.5,
22.5, 22.7, 23.0, 23.5, 24.0, 24.0, 24.6, 25.0, 25.6, 26.5,
27.3, 27.5, 27.5, 27.5, 28.0, 28.7, 30.0, 32.8, 34.5, 35.0,
36.5, 36.0, 37.0, 37.0, 39.0, 39.0, 39.0, 40.0, 40.0, 40.0,
40.0, 42.0, 43.0, 43.0, 43.5, 44.0]
)
perch_weight = np.array(
[5.9, 32.0, 40.0, 51.5, 70.0, 100.0, 78.0, 80.0, 85.0, 85.0,
110.0, 115.0, 125.0, 130.0, 120.0, 120.0, 130.0, 135.0, 110.0,
130.0, 150.0, 145.0, 150.0, 170.0, 225.0, 145.0, 188.0, 180.0,
197.0, 218.0, 300.0, 260.0, 265.0, 250.0, 250.0, 300.0, 320.0,
514.0, 556.0, 840.0, 685.0, 700.0, 700.0, 690.0, 900.0, 650.0,
820.0, 850.0, 900.0, 1015.0, 820.0, 1100.0, 1000.0, 1100.0,
1000.0, 1000.0]
)
|