Prepare data with Numpy
1 | fish_length = [25.4, 26.3, 26.5, 29.0, 29.0, 29.7, 29.7, 30.0, 30.0, 30.7, 31.0, 31.0, |
1 | import numpy as np |
[[ 25.4 242. ]
[ 26.3 290. ]
[ 26.5 340. ]
[ 29. 363. ]
[ 29. 430. ]]
1 | fish_target = np.concatenate((np.ones(35), np.zeros(14))) |
[1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.
1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0.]
Split data with Scikit-learn
1 | from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split |
1 | print(train_input.shape, test_input.shape) |
(36, 2) (13, 2)
(36,) (13,)
[0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
KNN 1
KNN fitting
1 | from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier |
1.0
Predicting new data
1 | print(kn.predict([[25,150]])) # the actual data is a bream, but predicted to be smelt. |
[0.]
1 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
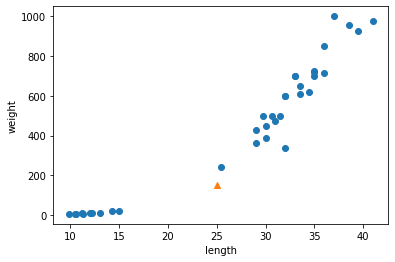
1 | distances, indexes = kn.kneighbors([[25,150]]) # the nearest neighbors (default: 5) |
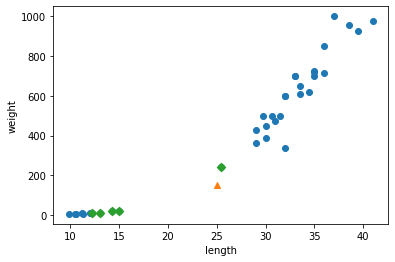
1 | # Scatter plot on the same scale |

KNN 2
Data Preprocessing
1 | # standard score |
1 | # Scatter plot with standard score |
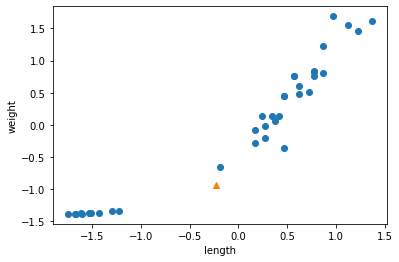
KNN fitting
1 | test_scaled = (test_input - mean) / std |
1.0
Predicting new data
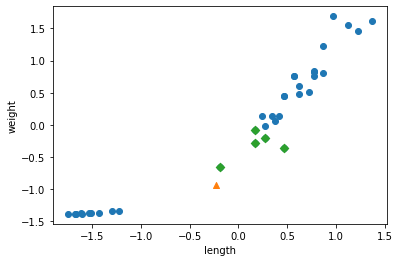
1 | print(kn.predict([new])) # the actual data is a bream, and predicted to be bream. |
[1.]
1 | distances, indexes = kn.kneighbors([new]) |
Ref.) 혼자 공부하는 머신러닝+딥러닝 (박해선, 한빛미디어)